Purpose
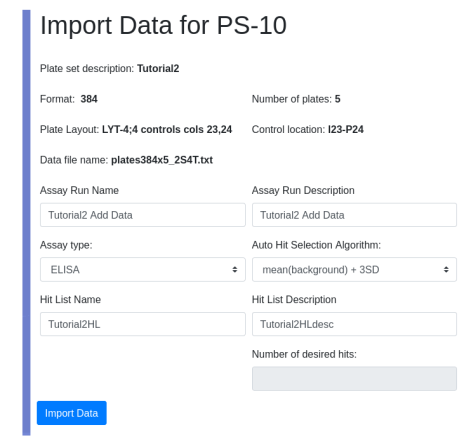
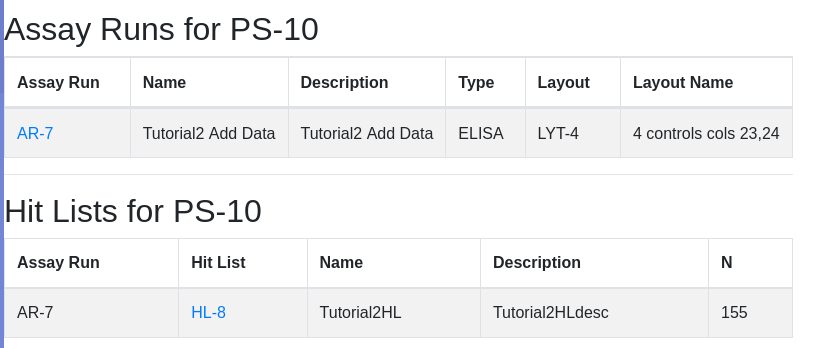
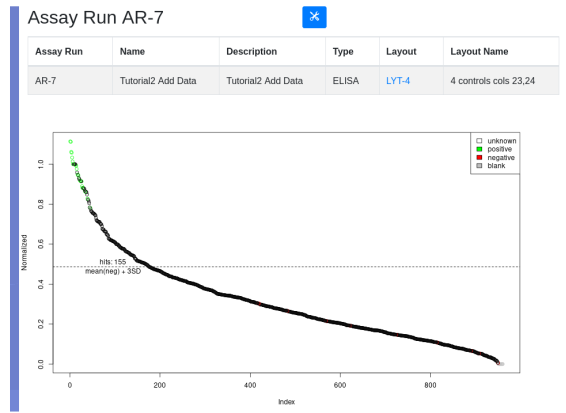
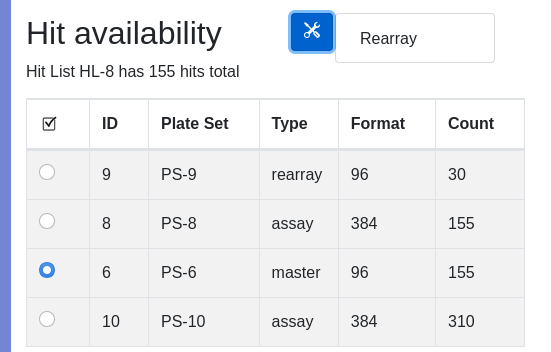
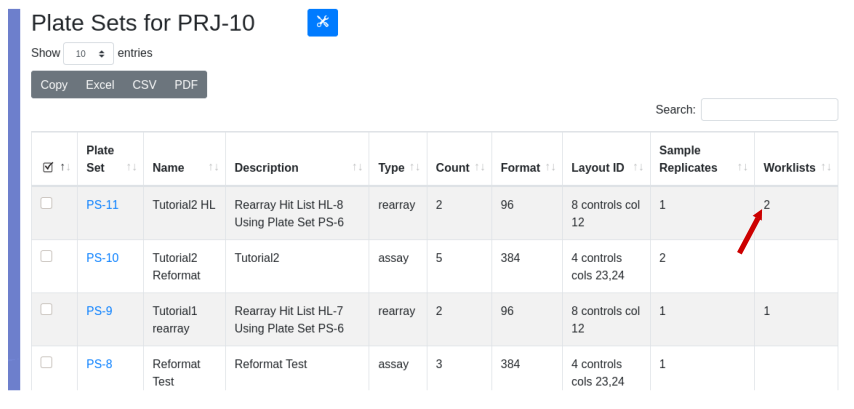
Ease your organization into Urbit by using the Urbit ID system to validate users. Use the Landscape viewer to distribute software - in this case a simple hyperlink to an internally developed web app. No hoon coding required. The web app must be modified to accept white listed Urbit IDs.
Prepare Linux
The following is a modification of the hello app found on developers.urbit.org. I am starting with a new instance of Debian 11 on AWS. Note that some of the commands below will need to be modified with your AWS credentials, configuration. This video walks through the process.
Update, install some utilities and create a swap space:
1 | sudo apt-get update |
edit fstab:
1 | sudo nano /etc/fstab |
add the following line:
1 | /swapfile swap swap defaults 0 0 |
Prepare new desk contents
Clone the required desks and merge them into your project desk OR git clone the limsn project and apply modifications. Note that this process slightly differs from developers.urbit.org which is out of date:
1 | projects$ git clone https://github.com/urbit/urbit urbit-git |
Modify the contents of desk.docket-0 to suit your needs:
1 | :~ title+'LIMS*Nucleus' |
The merged desks, auxilliary files and glob can be cloned, see below.
Prepare fake zod
Start up a fake zod, create and mount a new desk, delete the desk and git clone its replacement:
1 | curl -L https://urbit.org/install/linux-x86_64/latest | tar xzk --transform='s/.*/urbit/g' && ./urbit |
cd into zod and delete the new desk. git clone its replacement. The cloned directory contains the merged dev desks, desk.ship etc. as well as a glob:
1 | cd ./zod |
Get the glob out of the desk or the desk will not compile:
1 | $ mv ./zod/limsn/glob . |
On local machine transfer glob to local machine:
1 | scp -r -i labsolns.pem admin@ec2-3-145-214-48.us-east-2.compute.amazonaws.com:./glob . |
On zod:
1 | ~zod:dojo>|commit %limsn |
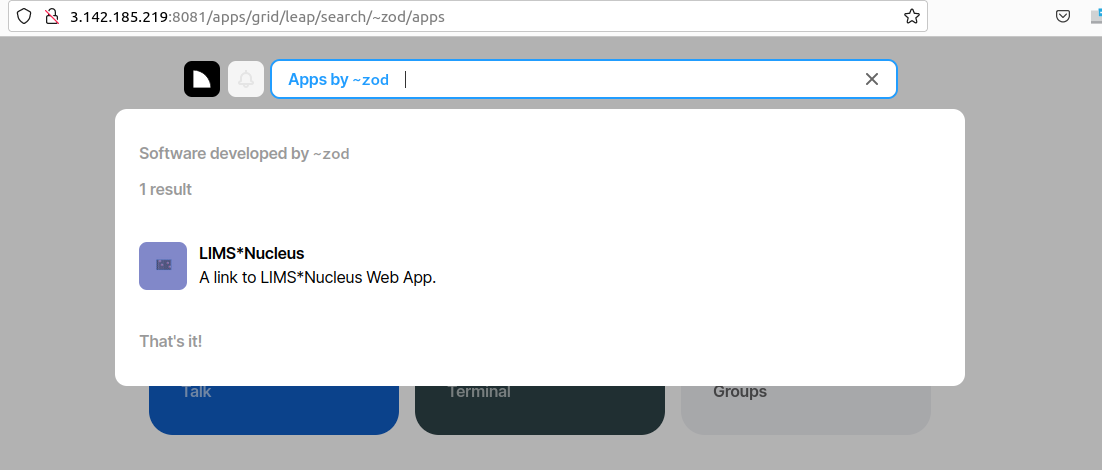
Assuming fake zod is on your local machine you can point your browser to localhost:8080 and see landscape with a new LIMS*Nucleus tile with spinner indicating “loading”. For AWS I use my temporary IP: http://3.142.185.219:8080.
To complete the install you must upload the glob. First modify index.html to suit your needs:
1 |
|
The javascript helper scripts are discussed in the http api guide. Note the ‘window.ship’ variable which provides the ship name (‘zod’ in this example) for appending to your web app’s urbit controller. In LIMS*Nucleus, urbit ids must be white listed in the ‘person’ table:
1 | lndb=> select * from person; |
Note the the urbit ID password hashes are a hash of the salt only as the password is blank. Urbit users come to the app prevalidated.
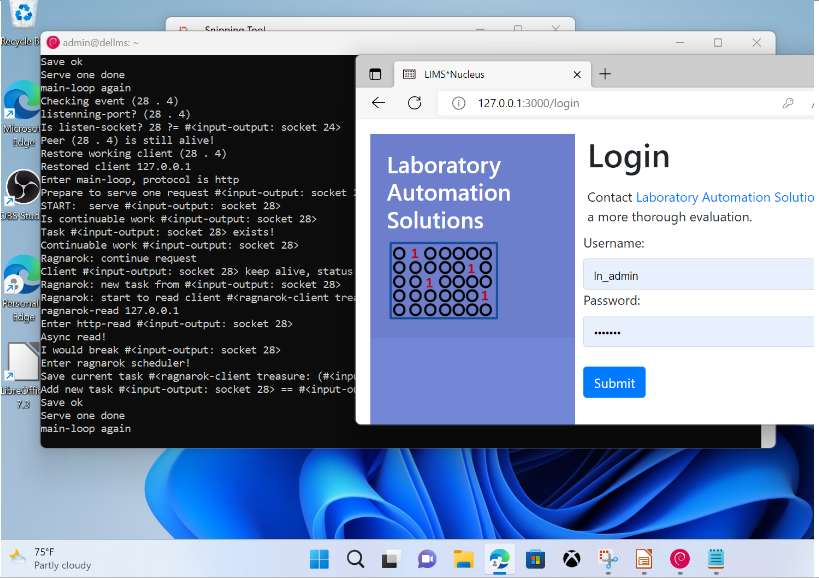
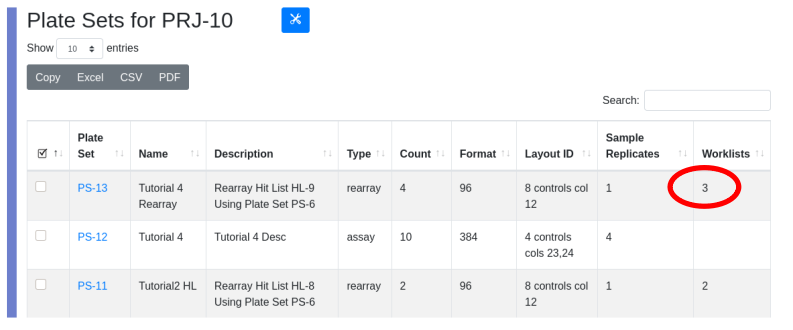
To upload the glob navigate to localhost:8080/docket/upload, select the limsn desk, press browse and select the glob directory and press the “glob!” button. Returning to zod you should now see:

Click on the LIMS*Nucleus tile and you will be redirected to the web app and logged in.
To allow zod to distribute this link, at the dojo:
1 | ~zod:dojo>:treaty|publish %limsn |
Now if I create a fake ~nus on the same instance of AWS but broadcast on port 8081, I can query ~zod on 8080 for software offered. We can piggyback on the Urbit desk distribution mechanism to distribute software - though in this example we are simply distributing a hyperlink allowing redirection: